
Continuing the special on invisible payments, it is relevant to talk specifically about biometric payments, or transactions with the face or fingerprint.
Fifty years ago a piece of cardboard with printed numbers revolutionized the way people pay. Today, although cash is still being used, there is talk of digital transactions to save time and costs.
So, the future of digital payments is heralded with solutions designed to be “simple, convenient and secure,” explains Daniel Aguilar, Veritran's vice president of Business Development for Latin America.
“The digitization of payments is called invisible payments, as well as the possibility of carrying out transactions using the face, called biometric payments, which promise to be the next global trend,” said the expert. But what is he talking about? Next, we will explain what biometric payments are and why they are the future both in digital banking and in the use of applications.
Today, users demand increasingly simple and natural shopping patterns, such as pointing voice commands or showing their faces in front of a cell phone screen.
To this end, biometric payments provide greater security and improve the user experience by quickly authenticating transactions using unique features analyzed by the technology, without violating the customer's identity.
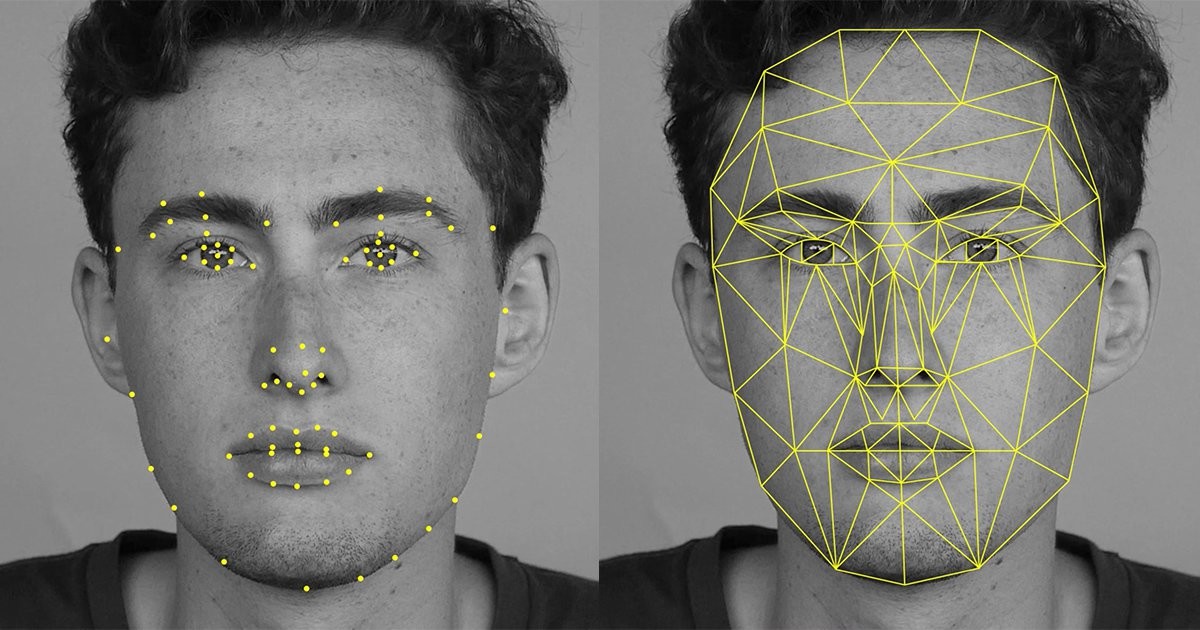
Biometrics allows us to compare the physical and behavioral characteristics of an individual, and is applied to digital banking, serving to confirm the authenticity of a transaction through very simple actions, as simple as using a fingerprint or looking at the camera.
“Facial biometrics doesn't keep a picture of your face. Save certain points of the face, and then perform a face match and compare 3D with 3D. For technology to identify what you really are, it depends on the policies of each country. In Mexico, for example, the regulation makes a text read in order to be able to authenticate that the person who will do an action is who they say they are. It also uses the typical methods that put a point to the user, start looking at it and that's it. There are many variations, depending on each country,” he explained to Infobae.
1. Convenience
Biometric payment technology allows consumers to determine their identity quickly, easily and easily. With a biometric card with fingerprint reader, the individual only needs to be physically present to make a purchase, no other information is required.
2. Safer
The use of biometric payment facilities provides greater security to customers and banks, thanks to the uniqueness of the biometric characteristics of each individual.
Before authorizing payment, the card compares the user's fingerprint presented to the scanner with the reference data stored securely on the card.
If the card is lost or stolen, it cannot be withdrawn or used, even for low-value contactless payments.
3. Reduce administrative work
Banks incur significant administrative costs when using traditional identification methods. Whether it's issuing a PIN, manufacturing a card reader at home, or verifying the identity of a new customer, verifying a customer's identity is expensive.
However, by using biometric banking, financial services organizations will be able to significantly reduce the administrative workload and streamline processes.
4. Quick customer registration
According to a study conducted by FICO, a leader in digital economic decision-making platforms in Mexico, 40% customers skip the registration process when applying for a new bank account.
When it comes to acquiring new customers, it's important that the process is fast. And that's where biometric technology helps in banking.
Through fingerprint or iris scanning, customers can quickly verify if they are who they say they are and immediately start using your services.

In which Latin American countries are biometric payments already used, and with which services
Mexico is definitely the most advanced country in using face payments. In the case of the country mentioned, services such as Uber, Beat, Cabify, Rappi and Globo already have the biometric payment method.
People who request one of these services, simply wait for a pizza to arrive, for example, and when the delivery man arrives at the user's home, they simply enter a mobile app to be able to scan the consumer's face and verify if they really are who they say they are, and if their affiliate cards are the same.
The same goes for Uber, Cabify or Beat. The passenger completes their journey and the driver, if the user previously has the card affiliated with the application, simply scans the face and the payment is made.

Finally, in countries such as Peru, Chile, Colombia, Argentina or Brazil, biometric payment technology is not yet available.
The main problem why it is not implemented regionally lies with devices, since having them on the street (supermarkets, stores, metro, among others), how to implement them on mobile phones is expensive. And sometimes dangerous because of the insecurity in certain places where cell phones are stolen.
On the other hand, with POS or QR code there is still a lack of development because of their cost or because they were not easy to find devices in different locations in a city or country.
“The drawback is the lack of technology for many countries in the Latin American region,” Aguilar concludes.
KEEP READING
Últimas Noticias
Debanhi Escobar: they secured the motel where she was found lifeless in a cistern

The oldest person in the world died at the age of 119

Macabre find in CDMX: they left a body bagged and tied in a taxi
The eagles of America will face Manchester City in a duel of legends. Here are the details

Why is it good to bring dogs out to know the world when they are puppies




